Becky Carroll was missing a few teeth, and others were stained or crooked. Ashamed, she smiled with lips pressed closed. Her dentist offered to fix most of her teeth with root canals and crowns, Carroll said, but she was wary of traveling a long road of dental work.
Then Carroll saw a TV commercial for another path: ClearChoice Dental Implant Centers. The company advertises that it can give patients “a new smile in as little as one day” by surgically replacing teeth instead of fixing them.
So Carroll saved and borrowed for the surgery, she said. In an interview and a lawsuit, Carroll said that at a ClearChoice clinic in New Jersey in 2021, she agreed to pay $31,000 to replace all her natural upper teeth with pearly-white prosthetic ones. What came next, Carroll said, was “like a horror movie.”
Carroll alleged that her anesthesia wore off during implant surgery, so she became conscious as her teeth were removed and titanium screws were twisted into her jawbone. Afterward, Carroll’s prosthetic teeth were so misaligned that she was largely unable to chew for more than two years until she could afford corrective surgery at another clinic, according to a sworn deposition from her lawsuit.
ClearChoice has denied Carroll’s claims of malpractice and negligence in court filings and did not respond to requests for comment on the ongoing case.
“I thought implants would be easier, and all at once, so you didn’t have to keep going back to the dentist,” Carroll, 52, said in an interview. “But I should have asked more questions … like, Can they save these teeth?”
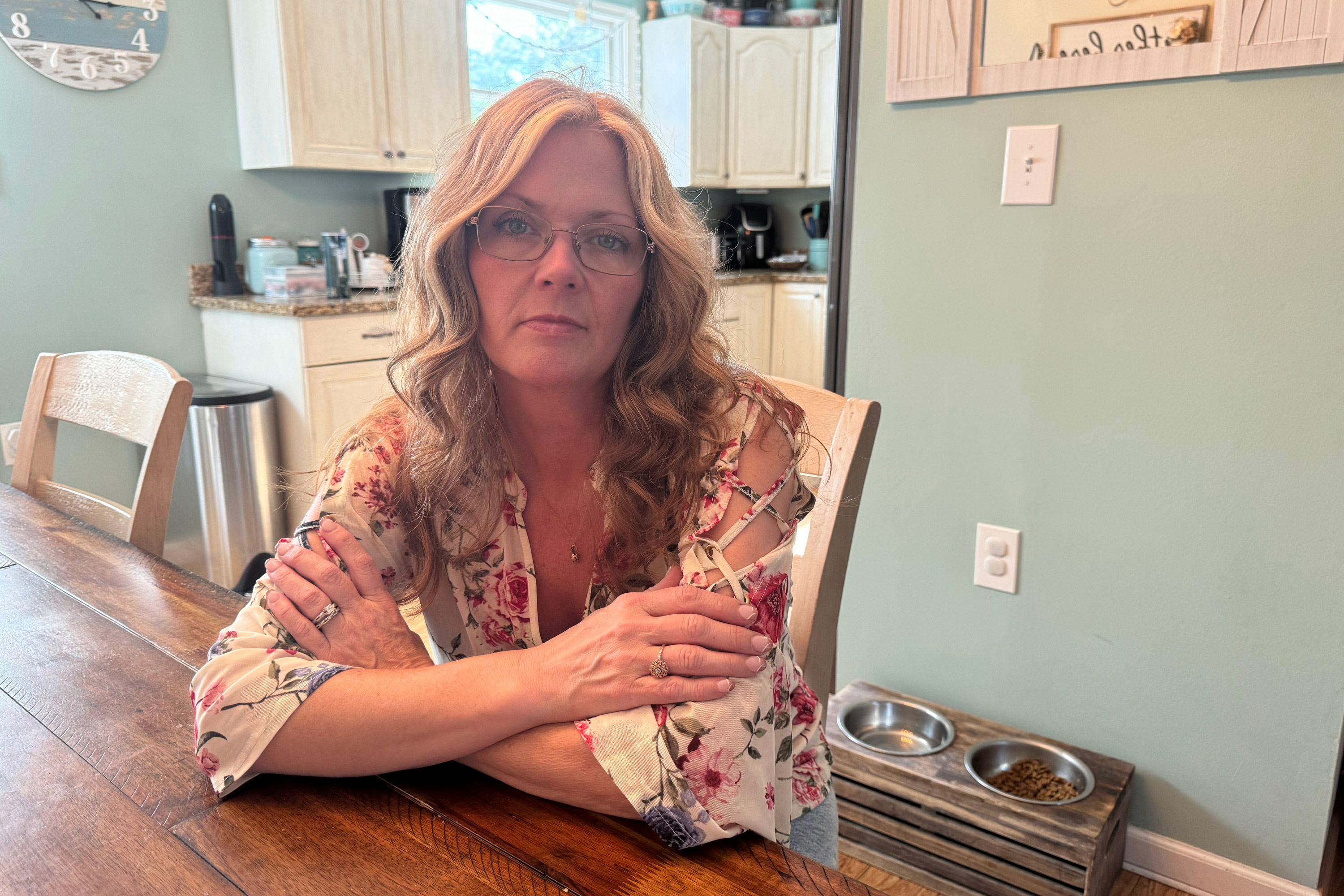 Becky Carroll of New Jersey has alleged in a lawsuit that she suffered a botched dental implant surgery in 2021, leaving her unable to chew for more than two years. ClearChoice Dental Implant Centers has denied all wrongdoing in the ongoing suit.(Nicole Keller/CBS News)
Becky Carroll of New Jersey has alleged in a lawsuit that she suffered a botched dental implant surgery in 2021, leaving her unable to chew for more than two years. ClearChoice Dental Implant Centers has denied all wrongdoing in the ongoing suit.(Nicole Keller/CBS News)Dental implants have been used for more than half a century to surgically replace missing or damaged teeth with artificial duplicates, often with picture-perfect results. While implant dentistry was once the domain of a small group of highly trained dentists and specialists, tens of thousands of dental providers now offer the surgery and place millions of implants each year in the U.S.
Amid this booming industry, some implant experts worry that many dentists are losing sight of dentistry’s fundamental goal of preserving natural teeth and have become too willing to remove teeth to make room for expensive implants, according to a months-long investigation by KFF Health News and CBS News. In interviews, 10 experts said they had each given second opinions to multiple patients who had been recommended for mouths full of implants that the experts ultimately determined were not necessary. Separately, lawsuits filed across the country have alleged that implant patients like Carroll have experienced painful complications that have required corrective surgery, while other lawsuits alleged dentists at some implant clinics have persuaded, pressured, or forced patients to remove teeth unnecessarily.
The experts warn that implants, for a single tooth or an entire mouth, expose patients to costs and surgery complications, plus a new risk of future dental problems with fewer treatment options because their natural teeth are forever gone.
“There are many cases where teeth, they’re perfectly fine, and they’re being removed unnecessarily,” said William Giannobile, dean of the Harvard School of Dental Medicine. “I really hate to say it, but many of them are doing it because these procedures, from a monetary standpoint, they’re much more beneficial to the practitioner.”
Email Sign-Up
Subscribe to KFF Health News' free Morning Briefing.
Giannobile and nine other experts say they are combating a false public perception that implants are more durable and longer-lasting than natural teeth, which some believe stems in part from advertising on TV and social media. Implants require upkeep, and although they can’t get cavities, studies have shown that patients can be susceptible to infections in the gums and bone around their implants.
“Just because somebody can afford implants doesn’t necessarily mean that they’re a good candidate,” said George Mandelaris, a Chicago-area periodontist and member of the American Academy of Periodontology Board of Trustees. “When an implant has infection, or when an implant has bone loss, an implant dies a much quicker death than do teeth.”
In its simplest form, implant surgery involves extracting a single tooth and replacing it with a metal post that is screwed into the jaw and then affixed with a prosthetic tooth commonly made of porcelain, also known as a crown. Patients can also use “full-arch” or “All-on-4” implants to replace all their upper or lower teeth — or all their teeth.
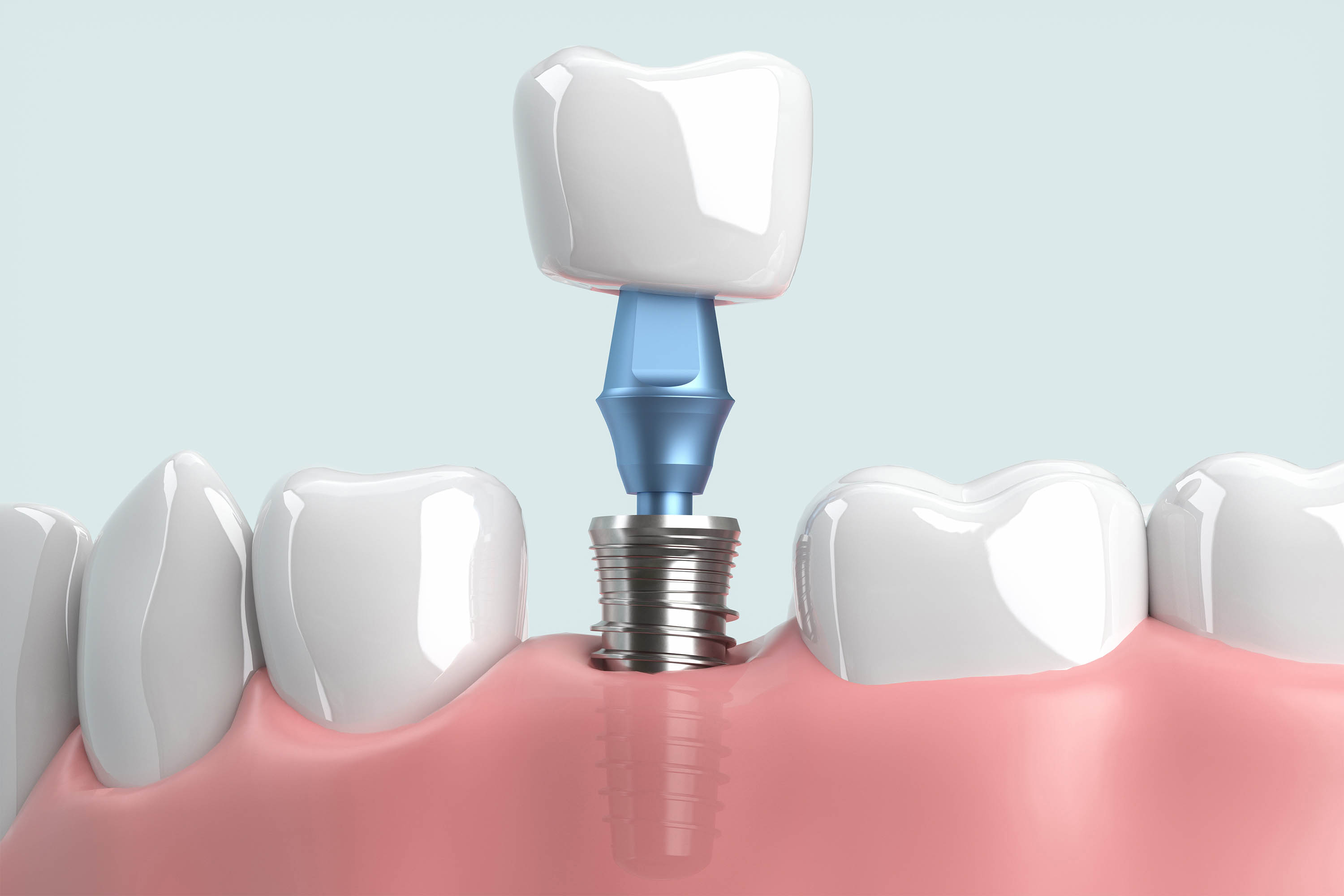 Dental implants have been used to replace damaged or missing teeth for decades. They generally consist of a metal anchor screwed into the bone, then capped with a prosthetic tooth, commonly made of porcelain.(Moment/Getty Images)
Dental implants have been used to replace damaged or missing teeth for decades. They generally consist of a metal anchor screwed into the bone, then capped with a prosthetic tooth, commonly made of porcelain.(Moment/Getty Images)For this story, KFF Health News and CBS News sought interviews with large dental chains whose clinics offer implant surgery — ClearChoice, Aspen Dental, Affordable Care, and Dental Care Alliance — each of which declined to be interviewed or did not respond to multiple requests for comment. The Association of Dental Support Organizations, which represents these companies and others like them, also declined an interview request.
ClearChoice, which specializes in full-arch implants, did not answer more than two dozen questions submitted in writing. In an emailed statement, the company said full-arch implants “have become a well-accepted standard of care for patients with severe tooth loss and teeth with poor prognosis.”
“The use of full-arch restorations reflects the evolution of modern dentistry, offering patients a solution that restores their ability to eat, speak, and live comfortably — far beyond what traditional dentures can provide,” the company said.
Carroll said she regrets not letting her dentist try to fix her teeth and rushing to ClearChoice for implants.
“Because it was a nightmare,” she said.
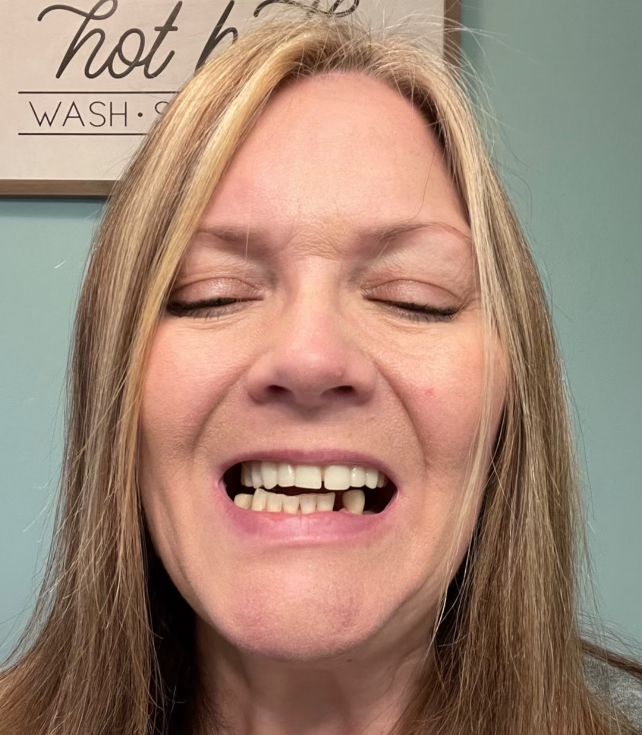 Carroll displays the dental implants she got in her upper jaw in 2021. She has alleged in a lawsuit against ClearChoice that her implants were misaligned with her bottom teeth, leaving her unable to eat solid food. ClearChoice has denied all wrongdoing in the lawsuit.(Rebecca Carroll)
Carroll displays the dental implants she got in her upper jaw in 2021. She has alleged in a lawsuit against ClearChoice that her implants were misaligned with her bottom teeth, leaving her unable to eat solid food. ClearChoice has denied all wrongdoing in the lawsuit.(Rebecca Carroll)‘They Are Not Teeth’
Dental implant surgery can be a godsend for patients with unsalvageable teeth. Several experts said implants can be so transformative that their invention should have contended for a Nobel Prize. And yet, these experts still worry that implants are overused, because it is generally better for patients to have their natural teeth.
Paul Rosen, a Pennsylvania periodontist who said he has worked with implants for more than three decades, said many patients believe a “fallacy” that implants are “bulletproof.”
“You can’t just have an implant placed and go off riding into the sunset,” Rosen said. “In many instances, they need more care than teeth because they are not teeth.”
Generally, a single implant costs a few thousand dollars while full-arch implants cost tens of thousands. Neither procedure is well covered by dental insurance, so many clinics partner with credit companies that offer loans for implant surgeries. At ClearChoice, for example, loans can be as large as $65,000 paid off over 10 years, according to the company’s website.
Despite the price, implants are more popular than ever. Sales increased by more than 6% on average each year since 2010, culminating in more than 3.7 million implants sold in the U.S. in 2022, according to a 2023 report produced by iData Research, a health care market research firm.
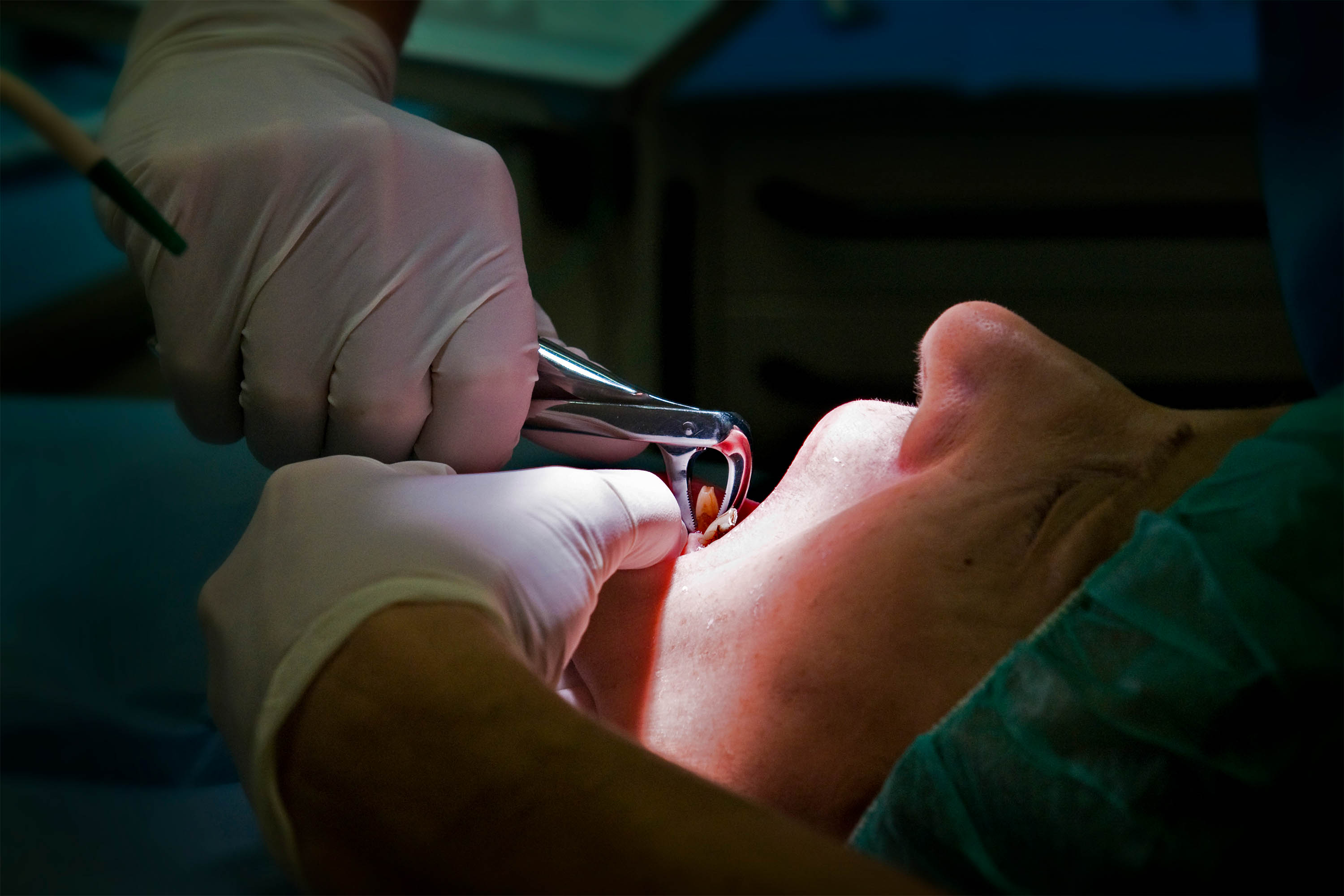 Dental implant surgery often involves extracting a patient’s natural tooth so it can be swapped for a prosthetic replacement. Patients can use “full-arch” or “All-on-4” dental implants to replace all their upper or lower teeth — or all their teeth.(Giovanni Mereghetti/UCG/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)
Dental implant surgery often involves extracting a patient’s natural tooth so it can be swapped for a prosthetic replacement. Patients can use “full-arch” or “All-on-4” dental implants to replace all their upper or lower teeth — or all their teeth.(Giovanni Mereghetti/UCG/Universal Images Group via Getty Images)Some worry implant dentistry has gone too far. In 10 interviews, dentists and dental specialists with expertise in implants said they had witnessed the overuse of implants firsthand. Each expert said they’d examined multiple patients in recent years who were recommended for full-arch implants by other dentists despite their teeth being treatable with conventional dentistry.
Giannobile, the Harvard dean, said he had given second opinions to “dozens” of patients who were recommended for implants they did not need.
“I see many of these patients now that are coming in and saying, ‘I’ve been seen, and they are telling me to get my entire dentition — all of my teeth — extracted.’ And then I’ll take a look at them and say that we can preserve most of your teeth,” Giannobile said.
Tim Kosinski, who is a representative of the Academy of General Dentistry and said he has placed more than 19,000 implants, said he examines as many as five patients a month who have been recommended for full-arch implants that he deems unnecessary.
“There is a push in the profession to remove teeth that could be saved,” Kosinski said. “But the public isn’t aware.”
Luiz Gonzaga, a periodontist and prosthodontist at the University of Florida, said he, too, had turned away patients who wanted most or all their teeth extracted. Gonzaga said some had received implant recommendations that he considered “an atrocity.”
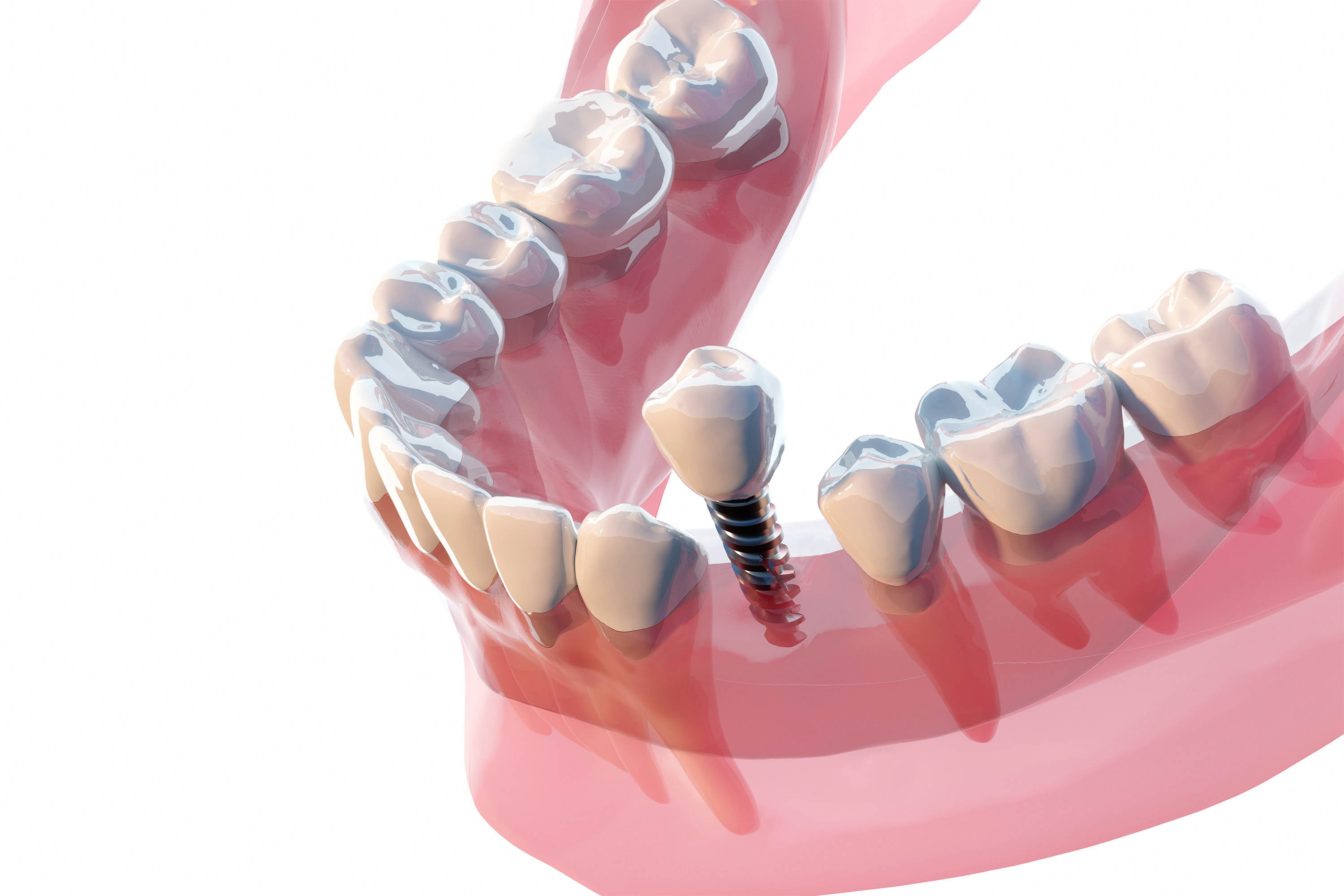 Dental implants are used to permanently replace damaged or missing teeth. They can restore a patient’s appearance and chewing ability. Implants are placed surgically and can’t be removed like most dentures.(Moment/Getty Images)
Dental implants are used to permanently replace damaged or missing teeth. They can restore a patient’s appearance and chewing ability. Implants are placed surgically and can’t be removed like most dentures.(Moment/Getty Images)“You don’t go to the hospital and tell them ‘I broke my finger a couple of times. This is bothering me. Can you please cut my finger off?’ No one will do that,” Gonzaga said. “Why would I extract your tooth because you need a root canal?”
Jaime Lozada, director of an elite dental implant residency program at Loma Linda University, said he’d not only witnessed an increase in dentists extracting “perfectly healthy teeth” but also treated a rash of patients with mouths full of ill-fitting implants that had to be surgically replaced.
Lozada said in August that he’d treated seven such patients in just three months.
“When individuals just make a decision of extracting teeth to make it simple and make money quick, so to speak, that’s where I have a problem,” Lozada said. “And it happens quite often.”
When full-arch implants fail, patients sometimes don’t have enough jawbone left to anchor another set. These patients have little choice but to get implants that reach into cheekbones, said Sohail Saghezchi, an oral and maxillofacial surgeon at the University of California-San Francisco.
“It’s kind of like a last resort,” Saghezchi said. “If those fail, you don’t have anywhere else to go.”
‘It Was Horrendous Dentistry’
Most of the experts interviewed for this article said their rising alarm corresponded with big changes in the availability of dental implants. Implants are now offered by more than 70,000 dental providers nationwide, two-thirds of whom are general dentists, according to the iData Research report.
Dentists are not required to learn how to place implants in dental school, nor are they required to complete implant training before performing the surgery in nearly all states. This year, Oregon started requiring dentists to complete 56 hours of hands-on training before placing any implants. Stephen Prisby, executive director of the Oregon Board of Dentistry, said the requirement — the first and only of its kind in the U.S. — was a response to dozens of investigations in the state into botched surgeries and other implant failures, split evenly between general dentists and specialists.
“I was frankly stunned at how bad some of these dentists were practicing,” Prisby said. “It was horrendous dentistry.”
Many dental clinics that offer implants have consolidated into chains owned by private equity firms that have bought out much of implant dentistry. In health care, private equity investment is sometimes criticized for overtreatment and prioritizing short-term profit over patients.
Private equity firms have spent about $5 billion in recent years to buy large dental chains that offer implants at hundreds of clinics owned by individual dentists and dental specialists. ClearChoice was bought for an estimated $1.1 billion in 2020 by Aspen Dental, which is owned by three private equity firms, according to PitchBook, a research firm focused on the private equity industry. Private equity firms also bought Affordable Care, whose largest clinic brand is Affordable Dentures & Implants, for an estimated $2.7 billion in 2021, according to PitchBook. And the private equity wing of the Abu Dhabi government bought Dental Care Alliance, which offers implants at many of its affiliated clinics, for an estimated $1 billion in 2022, according to PitchBook.
ClearChoice and Aspen Dental each said in email statements that the companies’ private equity owners “do not have influence or control over treatment recommendations.” Both companies said dentists or dental specialists make all clinical decisions.
Private equity deals involving dental practices increased ninefold from 2011 to 2021, according to an American Dental Association study published in August. The study also said investors showed an interest in oral surgery, possibly because of the “high prices” of implants.
“Some argue this is a negative thing,” said Marko Vujicic, vice president of the association’s Health Policy Institute, who co-authored the study. “On the other hand, some would argue that involvement of private equity and outside capital brings economies of scale, it brings efficiency.”
Edwin Zinman, a San Francisco dental malpractice attorney and former periodontist who has filed hundreds of dental lawsuits over four decades, said he believed many of the worst fears about private equity owners had already come true in implant dentistry.
“They’ve sold a lot of [implants], and some of it unnecessarily, and too often done negligently, without having the dentists who are doing it have the necessary training and experience,” Zinman said. “It’s for five simple letters: M-O-N-E-Y.”
Hundreds of Implant Clinics With No Specialists
For this article, journalists from KFF Health News and CBS News analyzed the webpages for more than 1,000 clinics in the nation’s largest private equity-owned dental chains, all of which offer some implants. The analysis found that more than 70% of those clinics listed only general dentists on their websites and did not appear to employ the specialists — oral surgeons, periodontists, or prosthodontists — who traditionally have more training with implants.
Affordable Dentures & Implants listed specialists at fewer than 5% of its more than 400 clinics, according to the analysis. The rest were staffed by general dentists, most of whom did not list credentialing from implant training organizations, according to the analysis.
 An Affordable Dentures & Implants location in the suburbs of Nashville, Tennessee. Affordable Dentures & Implants is part of Affordable Care, which was purchased by private equity firms for an estimated $2.7 billion in 2021.(Brett Kelman/KFF Health News)
An Affordable Dentures & Implants location in the suburbs of Nashville, Tennessee. Affordable Dentures & Implants is part of Affordable Care, which was purchased by private equity firms for an estimated $2.7 billion in 2021.(Brett Kelman/KFF Health News)ClearChoice, on the other hand, employs at least one oral surgeon or prosthodontist at each of its more than 100 centers, according to the analysis. But its new parent company, Aspen Dental, which offers implants in many of its more than 1,100 clinics, does not list any specialists at many of those locations.
Not everyone is worried about private equity in implant dentistry. In interviews arranged by the American Academy of Implant Dentistry, which trains dentists to use implants, two other implant experts did not express concerns about private equity firms.
Brian Jackson, a former academy president and implant specialist in New York, said he believed dentists are too ethical and patients are too smart to be pressured by private equity owners “who will never see a patient.”
Jumoke Adedoyin, a chief clinical officer for Affordable Care, who has placed implants at an Affordable Dentures & Implants clinic in the Atlanta suburbs for 15 years, said she had never felt pressure from above to sell implants.
“I’ve actually felt more pressure sometimes from patients who have gone around and been told they need to take their teeth out,” she said. “They come in and, honestly, taking a look at them, maybe they don’t need to take all their teeth out.”
Still, lawsuits filed across the country have alleged that dentists at implant clinics have extracted patients’ teeth unnecessarily.
For example, in Texas, a patient alleged in a 2020 lawsuit that an Affordable Care dentist removed “every single tooth from her mouth when such was not necessary,” then stuffed her mouth with gauze and left her waiting in the lobby as he and his staff left for lunch. In Maryland, a patient alleged in a 2021 lawsuit that ClearChoice “convinced” her to extract “eight healthy upper teeth,” by “greatly downplay[ing] the risks.” In Florida, a patient alleged in a 2023 lawsuit that ClearChoice provided her with no other treatment options before extracting all her teeth, “which was totally unnecessary.”
 After Aspen Dental bought ClearChoice for an estimated $1.1 billion in 2020, the companies began opening “co-location” clinics, like this one in Charlotte, North Carolina.(Fred Clasen-Kelly/KFF Health News)
After Aspen Dental bought ClearChoice for an estimated $1.1 billion in 2020, the companies began opening “co-location” clinics, like this one in Charlotte, North Carolina.(Fred Clasen-Kelly/KFF Health News)ClearChoice and Affordable Care denied wrongdoing in their respective lawsuits, then privately settled out of court with each patient. ClearChoice and Affordable Care did not respond to requests for comment submitted to the companies or attorneys. Lawyers for all three plaintiffs declined to comment on these lawsuits or did not respond to requests for comment.
Fred Goldberg, a Maryland dental malpractice attorney who said he has represented at least six clients who sued ClearChoice, said each of his clients agreed to get implants after meeting with a salesperson — not a dentist.
“Every client I’ve had who has gone to ClearChoice has started off meeting a salesperson and actually signing up to get their financing through ClearChoice before they ever meet with a dentist,” Goldberg said. “You meet with a salesperson who sells you on what they like to present as the best choice, which is almost always that they’re going to take out all your natural teeth.”
Becky Carroll, the ClearChoice patient from New Jersey, told a similar story.
Carroll said in her lawsuit that she met first with a ClearChoice salesperson referred to as a “patient education consultant.” In an interview, Carroll said the salesperson encouraged her to borrow money from family members for the surgery and it was not until after she agreed to a loan and passed a credit check that a ClearChoice dentist peered into her mouth.
“It seems way backwards,” Carroll said. “They just want to know you’re approved before you get to talk to a dentist.”
CBS News producer Nicole Keller contributed to this report.

















 English (US) ·
English (US) ·